- Obtain approval for the budget.
- Develop different budget scenarios.
- Ensure the necessary reserves are made available.
2 hours CPD
A7.KCI-2 Establish the Project Budget
Budgeting builds directly on cost estimation. Once project costs are estimated, they must be structured into a budget that is tied to both the work breakdown structure (WBS) and the cost breakdown structure (CBS).
By linking costs to activities and timelines, the project manager can forecast:
- When costs will occur
- What they will be spent on
- Whether sufficient funding and cash flow exist to support delivery
- gain a clear picture of time-related cash outflows and
- can also forecast cash inflows early in the project
A well-prepared budget also includes reserves to address risks, uncertainties, or potential scope changes.
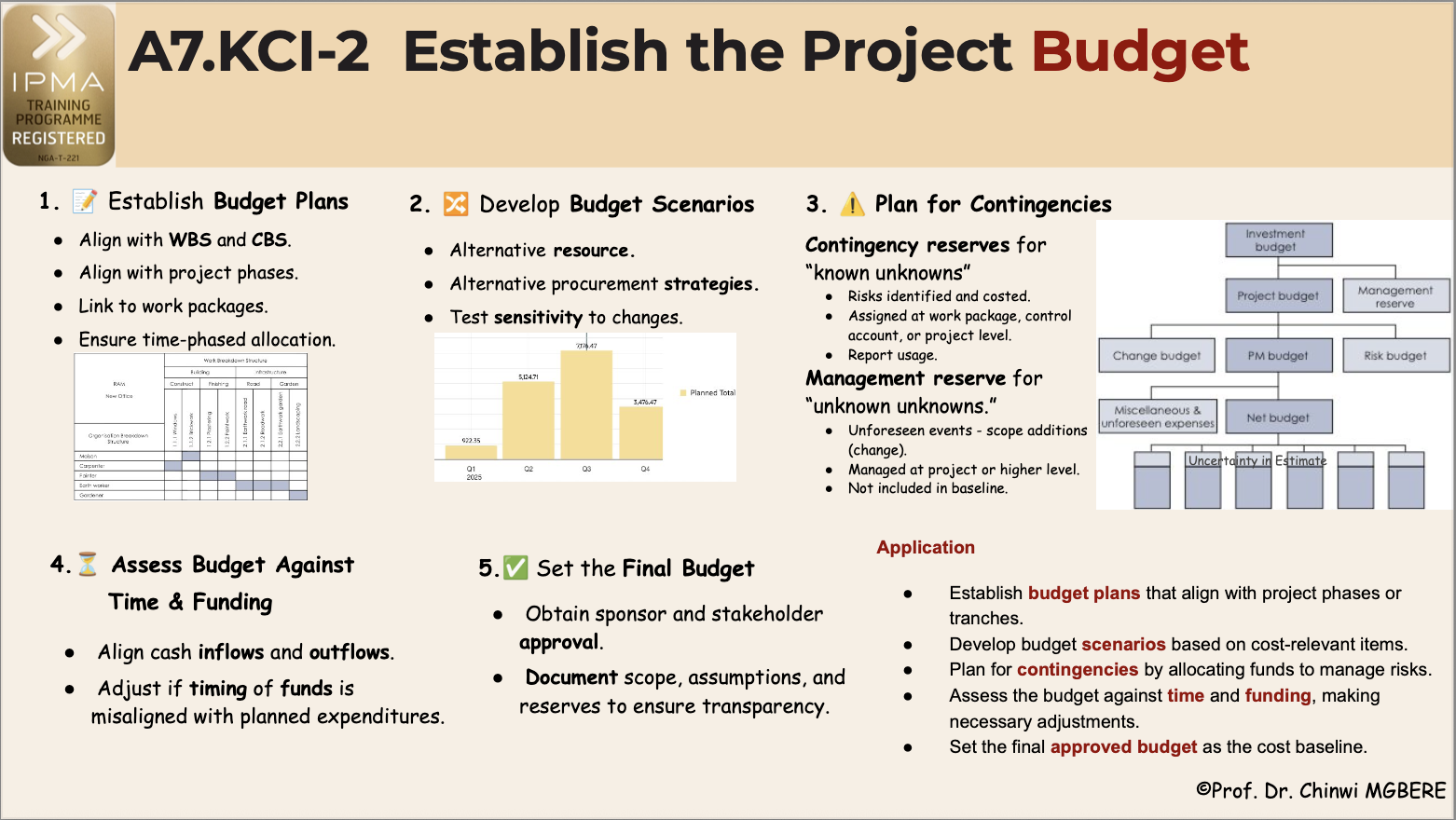
1. Establish Budget Plans
Define the overall budget structure aligned with the WBS and CBS.
- Align budget with project phases
- Link budget items to work packages and deliverables.
- Ensure time-phased allocation so expenditures can be tracked against progress.
2. Develop Budget Scenarios
Prepare different budget scenarios based on cost-relevant items.
- Include alternative resource or procurement strategies.
- Test sensitivity to changes in assumptions (e.g., rates, productivity, inflation).
3-1. Plan for Contingencies
Allocate funds for contingency reserves (“known unknowns”).
- These cover risks that have been identified and costed.
- Reserves may be assigned at the work package, control account, or project level.
- Always report contingency usage against actuals for transparency.
3-2. Include a Management Reserve
Set aside a management reserve for “unknown unknowns.”
- Intended for unforeseen events such as scope additions.
- Managed at the project/programme/portfolio level.
- Not included in baseline variance reporting until formally released.
4. Assess Budget Against Time & Funding
Review the budget in relation to the project schedule and organizational funding capacity.
- Align cash inflows and outflows.
- Adjust if the timing of funds is misaligned with planned expenditures.
5. Set the Final Budget
Consolidate all elements—base budget, contingencies, and management reserves—into the final approved budget.
- Obtain sponsor and stakeholder approval.
- Clearly document scope, assumptions, and reserves to ensure transparency.
To apply these actions to your current initiative, follow these steps:
- Establish budget plans that align with project phases or tranches.
- Develop budget scenarios based on cost-relevant items.
- Plan for contingencies by allocating funds to manage risks.
- Assess the budget against time and funding, making necessary adjustments.
- Set the final approved budget as the cost baseline.
Now, Let’s Test Your Knowledge


