- Determine the actual effort.
- Identify which resources you need.
- Make a choice as to who you are going to request.
2 Hours (CPD)
A3.KCI-2. Determine the necessary effort and duration
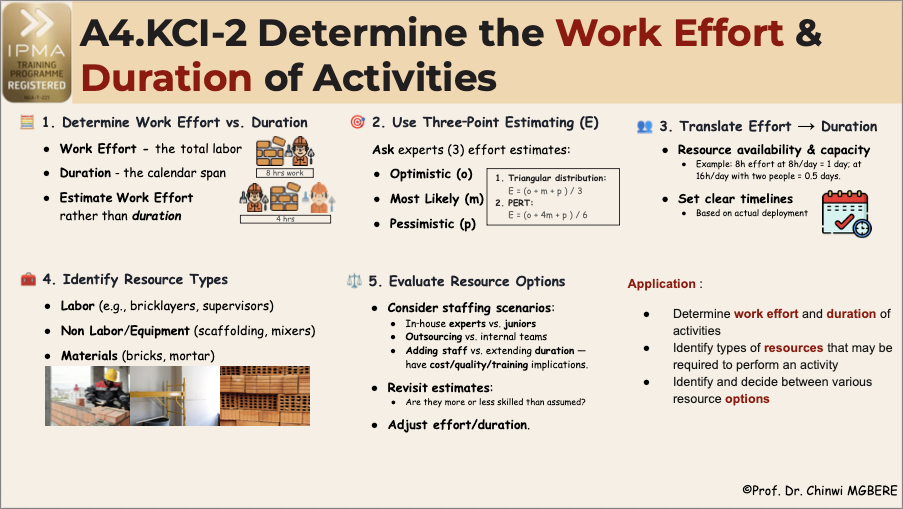
1. Determine Work Effort vs. Duration
Understanding the distinction between work effort and activity duration is essential for accurate project planning.
- Work effort represents the total labor required—often quantified in person-hours—to complete a task,
- while duration denotes the elapsed calendar time, which varies depending on resource allocation and availability.
- For example, an 8‑hour bricklaying task can be completed in just 4 hours when two bricklayers are assigned.
- Estimating effort first provides a stable basis for timelines, and combining it with resource data determines realistic durations—minimizing schedule padding and aligning expectations with actual capacity
2. Use Three Point Estimating
Ask experts for three effort estimates:
- Optimistic (O) — everything goes well
- Most Likely (M) — typical scenario
- Pessimistic (P) — worst-case
Compute expected effort using:
- Triangular distribution:
- Beta distribution (or PERT) distribution:
- E = (o + 4m + p ) / 6 (This weights the most likely scenario more heavily)
This method accounts for uncertainty, avoids padding, and results in “challenging but realistic” schedules. It aligns with Parkinson’s Law—that work expands to fill available time.
3. Translate Effort into Duration
Translating effort into duration depends on resource availability and staff capacity. For example: 8h effort at 8h/day = 1 day; at 18h/day with two people = 0.5 day.
Use these details to set clear timelines based on your team’s actual deployment.
4. Identify Resource Types
- List skills and categories needed for each activity:
- Labor (e.g., bricklayers, supervisors)
- Materials (bricks, mortar)
- Equipment (scaffolding, mixers)
- Think about proficiency, seniority, speed, and availability relative to your initial assumptions.
5. Evaluate Resource Options
- Consider different staffing scenarios:
- In-house experts vs. juniors
- Outsourcing vs. internal teams
- Adding staff vs. extending duration—each has cost/quality/training implications.
- Revisit your estimates once the team is assigned: are they more or less skilled than assumed? Adjust effort/duration accordingly.
To apply these actions to your current initiative, follow these steps:
- Determine work effort and duration of activities by gathering effort estimates and translating them into duration. Consider skill level, availability, and productivity.
- Identify types of resources that may be required to perform an activity, for example, skilled labor, tools and equipment, and materials.
- Identify and decide between various resource options by modeling various effort-to-duration conversions. For example, differences in experience or availability can alter duration.
Now, Let’s Test Your Knowledge


